KRISO receives AiP from ABS for Hydrogen Production Platform
□ The Korea Research Institute of Ships and Ocean Engineering (KRISO, President Keyyong Hong) reported on July 20, 2023 that KRISO had acquired Approval in Principle (AIP) for its hydrogen production platform from the American Bureau of Shipping (ABS).
□ The hydrogen production platform developed by KRISO, an eco-friendly platform for producing green hydrogen utilizing the electric power generated from renewable ocean energy, consists of ▲ a desalination system for converting sea water to fresh water, ▲ an electrolysis system for producing hydrogen through water electrolysis, ▲ a compression system for compressing the produced hydrogen, and ▲ a compressed hydrogen storage system for storing the compressed hydrogen.
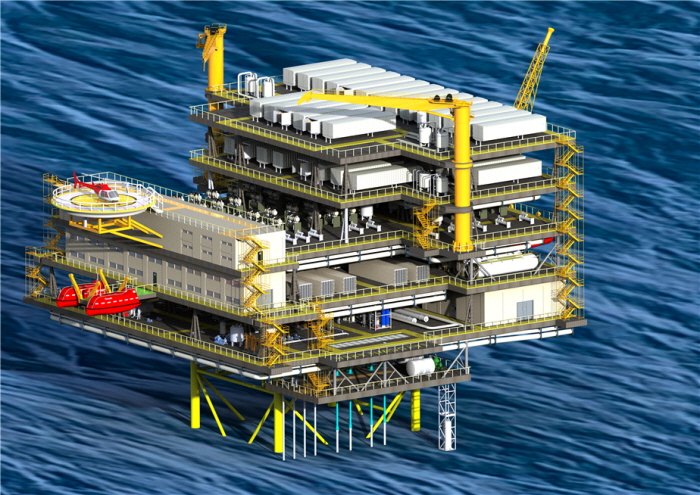

<concept drawing="" of="" the="" hydrogen="" production="" platform=""></concept>
□ The AIP acquired from ABS officially certified the safety and feasibility of the concepts of the hydrogen production platform systems developed by KRISO.
□ As the international community is intensifying greenhouse gas emission reduction targets or relevant regulations, non-carbon fuels such as methanol, ammonia, and hydrogen are rapidly emerging as next-generation eco-friendly energy resources.
□ In particular, hydrogen is drawing much attention as a carbon-free and pollution-free fuel. As hydrogen is applicable to various industries, including ships, automobiles, trains, and power generation, demand is expected to grow rapidly.
□ Most of the currently produced hydrogen is gray hydrogen, which is extracted by a reaction of natural gas with high-temperature and high-pressure steam or which is incidentally produced from the petrochemical processes. Therefore, carbon dioxide is also emitted in the production procedures.
□ On the other hand, the ocean renewable energy-based green hydrogen is produced utilizing electricity generated from eco-friendly ocean energy sources such as offshore wind power and wave power. This allows for the production of clean hydrogen without carbon emissions.
□ In addition, a large-scale hydrogen production complex can be formed by utilizing extensive offshore space resources. Wind power is particularly useful in the production of large amounts of hydrogen, because wind speed and wind power density are more favorable to hydrogen production on the sea than on the ground.
□ KRISO has joined in the UBJIP* for the development of the international standards for offshore plants, making efforts in joint research on and the preparation of international standards for hydrogen production platforms. For more efficient transportation of produced hydrogen, KRISO is actively conducting R&D work on an offshore platform for converting hydrogen to ammonia and liquid hydrogen.
* UBJIP (Unified Bulk Joint Industry Project): A consortium established in 2015 for preparing international standards for offshore plants, including HD Hyundai Heavy Industries, Samsung Heavy Industries, classification societies (DNV·ABS·BV·LR), KRISO, Korea Offshore & Shipbuilding Association, and Fire Insurers Laboratories of Korea.
□ Meanwhile, KRISO has made earnest efforts to develop technologies for utilizing various non-carbon fuels by ▲ acquiring AIP for a liquid hydrogen fuel tank from the Korean Register (KR) and developing the new tank technology selected by the Ministry of Oceans and Fisheries, ▲ acquiring AIP for the ammonia supply system of ammonia tankers from Loyd’s Register (LR), and ▲ acquiring AIP for LNG fueled container ships from LR. Furthermore, KRISO has recently begun the collaboration with ABS to develop technologies for methanol fueled ships.
□ KRISO’s President Keyyong Hong said, “As the global energy supply system is shifting from the conventional fossil fuels to eco-friendly renewable energy sources, we at KRISO will do our best to develop technologies for the ocean renewable energy-based production of clean hydrogen. We will continuously make efforts to develop technologies related to various non-carbon fuels and provide support to the industry.”

 Research Project
{{data.S ? data.S.sum : 0}}
Research Project
{{data.S ? data.S.sum : 0}}

 Patent
{{data.P ? data.P.sum : 0}}
Patent
{{data.P ? data.P.sum : 0}}
 Technology Transfer
{{data.T ? data.T.sum : 0}}
Technology Transfer
{{data.T ? data.T.sum : 0}}

 Thesis
{{data.R ? data.R.sum : 0}}
Thesis
{{data.R ? data.R.sum : 0}}